Wu and Carson [35] aimed at making the SRTM basis function approach even more robust and called it Simplified Reference Tissue Model 2 (SRTM2). They noted that with SRTM k2' is calculated with each pixel TAC, although the same reference TAC is used for all pixels. Therefore they implemented a two-step approach:
The operational equation of the SRTM was re-written to allow for fixing of k2'
![]()
The three parameters R1, k2a and k2' are estimated in step 1. In step 2 k2' is fixed, and only R1 and k2a are estimated. k2a is the apparent k2 (k2a = k2 /(1+BP)).
The binding potential can then be calculated as
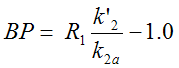
SRTM2 is based on the same assumptions as SRTM:
Note: As with the SRTM method, BP estimates from SRTM2 tend to be biased if the 1-tissue compartment model assumption does not apply. The magnitude of the bias is even larger for the SRTM2 estimates, most likely because the fixed k2' can not compensate a part of the model inadequacy [35].