Enabling Pre-Processing Operations
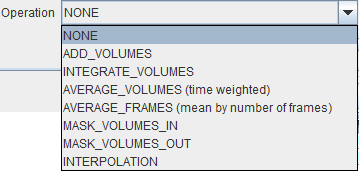
In addition to image reorientations there are several optional preprocessing methods available. On the INITIAL OPERATIONS tab the Operation selection provides the operations shown below.
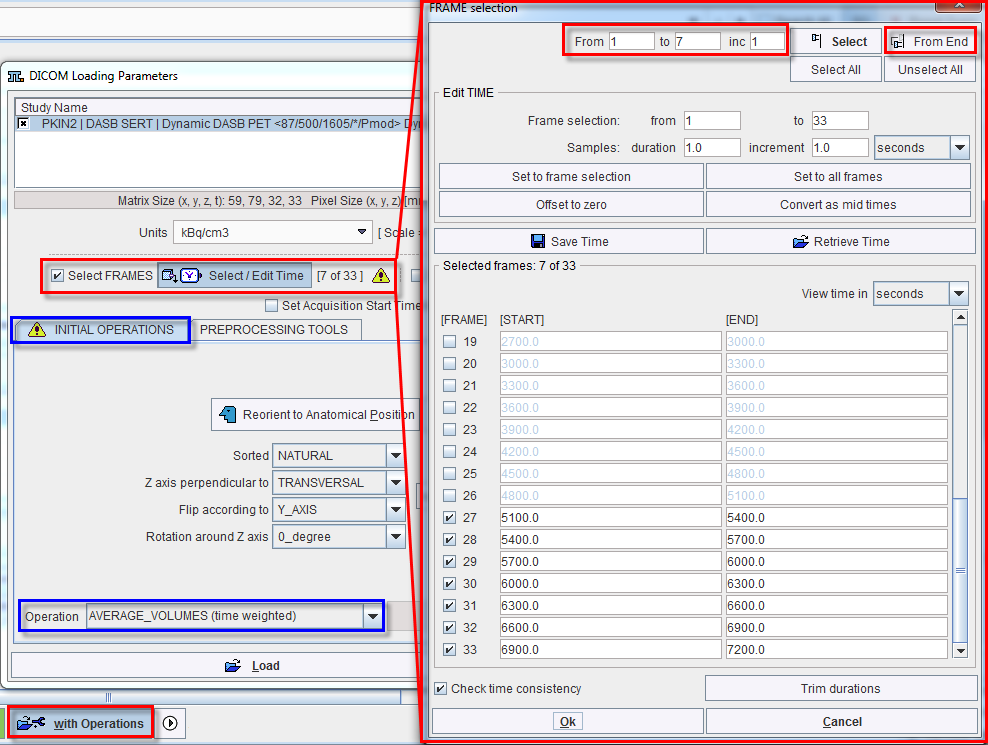
The example below illustrates how the last seven acquisitions of a dynamic study can be averaged by selecting the frames sub-range and setting the Operation selection from NONE to AVERAGE_VOLUMES (time weighted).
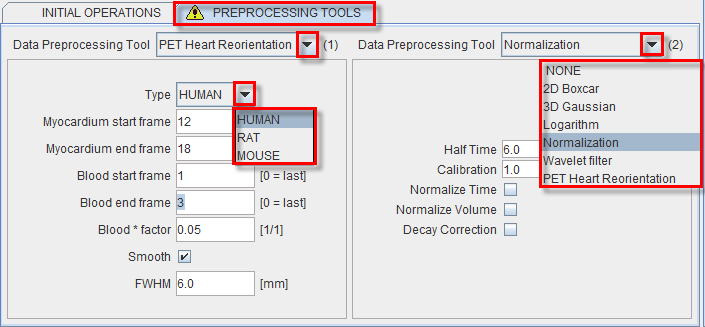
The tab PREPROCESSING TOOLS makes available two successive filters and a reorientation facility for the heart studies as illustrated below.
The purpose of Normalization is to transform reconstructed counts into activity density values calibrated in kBq/cc. The following parameters are needed for the calibration process:
- Half Time is used for a correction of the physical decay to the acquisition start. If the SPECT counts are already decay corrected, set Half Time to a big value to avoid an additional correction.
- Calibration is a factor for the conversion of the measured SPECT counts - which represent only a fraction of the emitted photons - into the true number of physical decays.
The calibration factor can be determined using a phantom filled with a known, representative activity concentration. Phantom images are acquired, corrected and reconstructed using the same protocol as the research study. Then, the image values are decay corrected, time and volume normalized, resulting in images with SPECT counts per ml per second. As the next step, a homogeneous VOI is outlined and the average pixel value calculated. Finally, the calibration factor is calculated by dividing the known true phantom activity concentration by the VOI average. - Normalize Time is a flag indicating whether the values in the file are already average counts per time (.ie. not total accumulated counts during the acquisition). If your image files just contain counts, check this box, and the image values are divided by the acquisition duration.
- Normalize Volume is a flag indicating whether the values are already counts per unit volume. If not, check this box, and the values are divided by the image voxel size (known from the image header).
- Decay Correction: Apply a decay correction to scan start.
Note: The preprocessing tools are plug-ins and must be configured in the main configuration dialog.
The PET Heart Reorientation is a facilty that allows heart images re-orientation in short axis during loading. The following parameters need to be defined:
- Type is representing the heart model type and can be selected from the available selection list: HUMAN, RAT or MOUSE according to the image to be analyzed.
- Myocardium start frame and Myocardium end frame are used to define the frames average range for creating the myocarium averaged image.
- Blood start frame and Blood end frame are used to define the frames average range for creating the blood averaged image.
- Blood*factor: as there may exist some activity in the cavities, a fraction of the blood volume image can be subtracted to improve the contrast. In the example above a fraction of 0.05 of the blood averaged image will be subtracted.
- Smooth and FWHM: optionally, the blood and myocardium averaged image can be smoothed with a 3D Gaussian filter with full-width half maximum value defined in the FWHM text box.


