The Kinetic menu contains an entry Parameters Aggregation. Its purpose is to concentrate the parameter values which have been saved in KM Parameters Files (*.kinPar) for statistical analysis. It opens a dialog window with two tabs as illustrated below.
Component Selection
The Select pane allows defining the files from which the parameters are extracted.
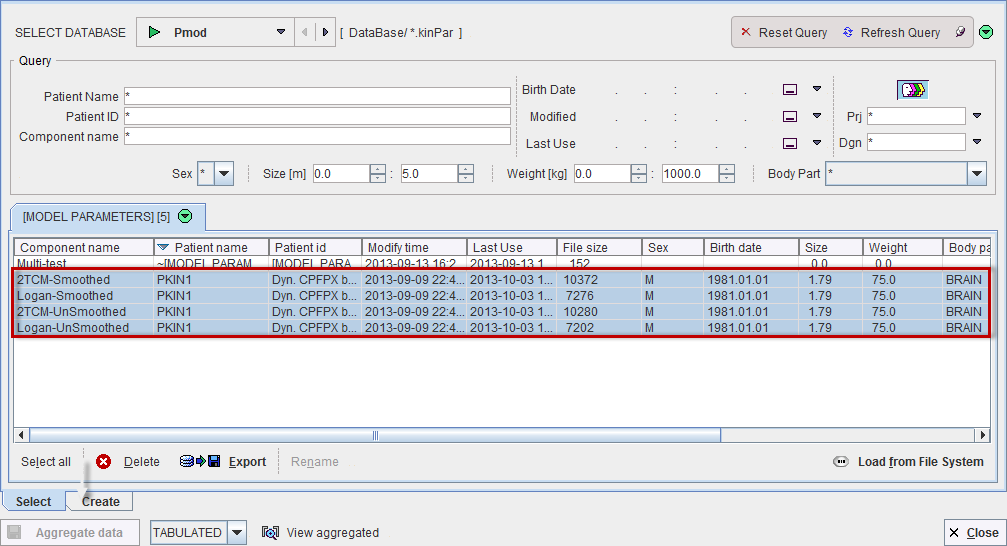
They may be available in a database as in the example above, or in a disk directory. In the latter case use Load from File System to define the directory were the files reside. All appropriate .kinPar data sets are listed. Select all data sets to be used for the aggregation and then switch to the Create pane.
Parameter Definition
The upper part of the Selected Components list shows which data sets have been selected for aggregation.
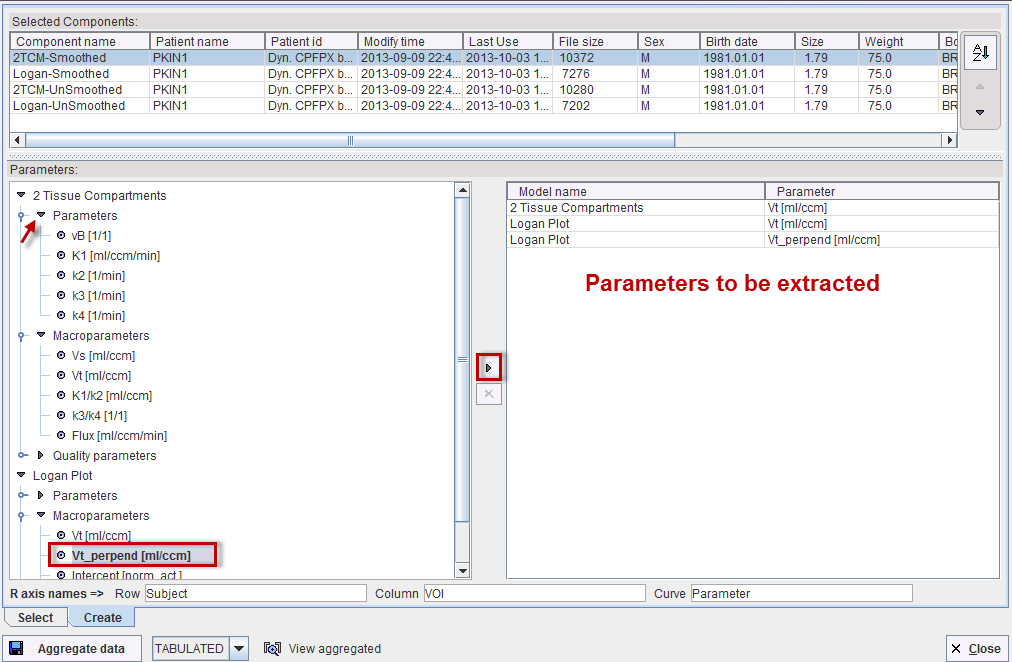
The Parameters section has a tree structure and initially shows the different types of models which have been used in any of the data sets. The parameters and fitting criteria of these models are organized in a tree structure which can be expanded and collapsed by clicking at the arrows.
To add a parameter to the aggregation list select it in the tree and activate the right arrow. Note that the copy operation works on all levels of the tree, so that with the top node selected, all parameters are copied at once.
Data Aggregation
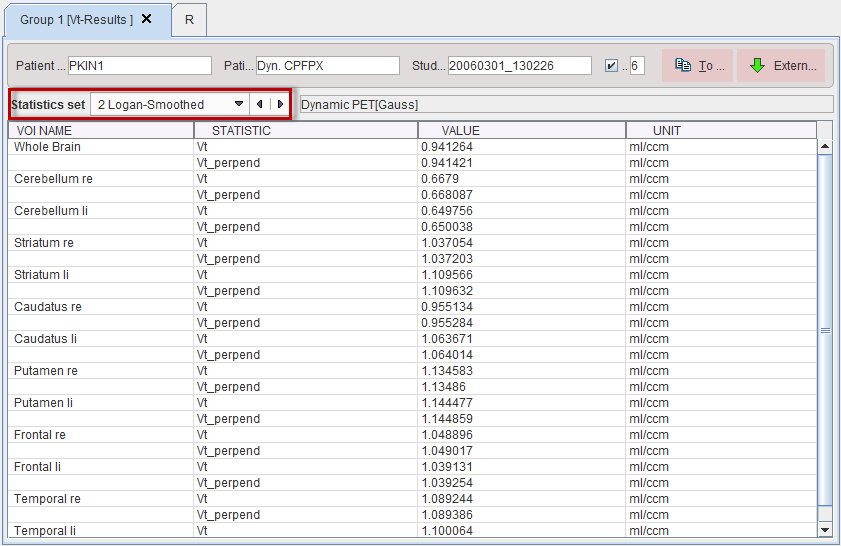
There are two aggregation formats available, EXCEL and TABULATED. Activating Aggregate data starts the aggregation process and asks for then name of a database table, or a file name if the database is not used. When opening the saved aggregate with the View aggregated button, the statistics window appears with a selection for the Statistics set. Note that results not available in all models are set to NaN.
Application Cases
It depends on the application case, what data is pooled into an aggregate. A typical example is the aggregation of the results of a population in a test study an a test aggregate, and the results of the same population in a retest study into a retest aggregate. These aggregates can then directly be used for a test-retest analysis.
Another result is the comparison of analysis methods. In this case the results of the different methods would be aggregated in corresponding aggregates, which can then be compared with a Bland-Altman analysis.