Reslicing after Loading
When loading an input study, the images automatically get resliced to the Reference resolution, whereby the program tries to align the two studies. If there are common DICOM landmarks available (Origins), they are aligned, otherwise the centers of the two data volumes are aligned. The result of this initial reslicing is shown in the CoReg area in the lower left fused with the Reference image. If multiple studies are loaded, this procedure is performed for each input independently.
The results of the matching initialization can be inspected in the CoReg panel by clicking at different points in the images. Note that they are synchronized with the upper reference images (as long as Synchronization box from the bottom status line is checked). The Color Synchronization check box allows linking the color tables of the fused images in the CoReg area with that of the original the Reference and Input images.
Automatic Initialization Variants
The Matching Initialization panel provides options to easily modify the properties of initial reslicing.
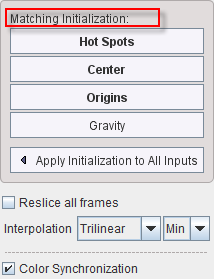
The following buttons are available. If the initial alignment is poor, please try them out to get a better result to start with.
Hot Spots |
This button needs to be used in combination with the orthogonal views of the Reference and the Reslice studies. The cross indicating the hot spot should be placed at the same anatomical landmark, as illustrated below. |
Center |
This button brings the centers of both data volumes into agreement. It is the preferred mode if the coordinate origins are distinct, but the studies cover (about) the same anatomical volume. |
Origins |
This button brings the origin of the coordinate system in both data sets into agreement. It works successfully if the same origin based on a common landmark has been defined in both studies, e.g. in a hybrid PET/CT study. |
Gravity |
This button brings the origin of the centers of mass in both data sets into agreement. |
All of these initialization buttons calculate and apply an initial Move transformation, which can be inspected in the panel.
Interactive Adjustments of Initialization
If none of the automatic initializations provides a reasonable starting point for the automatic procedure, the alignment can easily be manually adjusted. To this end activate the button in the CoReg image area illustrated below.
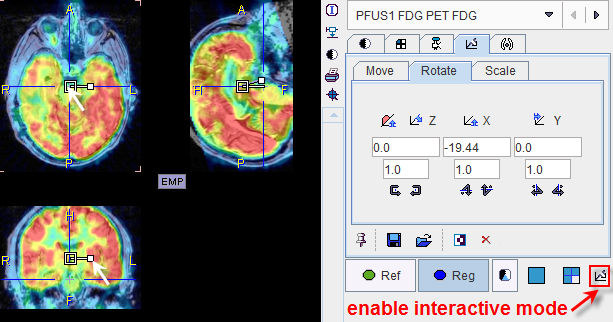
Now the selected reslice series can be shifted and rotated using the corresponding handles, as explained in more detail below.
Manual Initialization
The reslicing panel of the Reg image illustrated above shows the result of the initialization operation. However, the transformation parameters can also be set manually, for instance if the images to be registered always have the same constant offset. In these cases the initialization can be saved using the Save icon ![]() once, and then retrieved using the Load
once, and then retrieved using the Load  buttons the next time images have to be matched. Note that these settings can be applied to all loaded images with the Apply Initialization to All Inputs button.
buttons the next time images have to be matched. Note that these settings can be applied to all loaded images with the Apply Initialization to All Inputs button.
Dynamic Image Series
Dynamic series may become huge when resliced to anatomical reference images with high resolution. Therefore, with the Reslice all frames box, the reslicing behavior can be modified. If the box is checked, all frames of the dynamic input series will be resliced to the reference, creating again a dynamic series. If the box is not checked, only the frame currently selected in the Input area is resliced, resulting in a static series. This is the recommended mode at least for the initialization phase.
Results Interpolation
The Interpolation method choice lets the user define how image values are interpolated from the original pixel values when new slices are calculated. Default is Trilinear which is a simple and fast interpolation using all 8 enclosing pixel values. The truncated sinc interpolations Sinc (Window 5) and Sinc (Window 7) are more accurate, but considerably slower. Nearest neighbor interpolation just uses the value of the closest pixel, so it is very fast but in most cases does not provide satisfactory quality. However, it is the method of choice if an object map image containing integer values needs to be resliced.
The appropriate interpolation value for pixels which were outside the original field-of-view is unknown. Per default a value of 0 is applied, but the behavior can be changed to use the minimum of the data set (Min selection) which is more adequate for CT data.
Note that the interpolation choice has an impact on all calculations in the fusion tool.